CULTIVATION OF NISSAN REISHI
Natural Cycle
Nissan Chemical emphasizes the fruit body cultivation of reishi
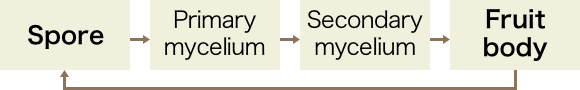
The life cycle of the mushroom
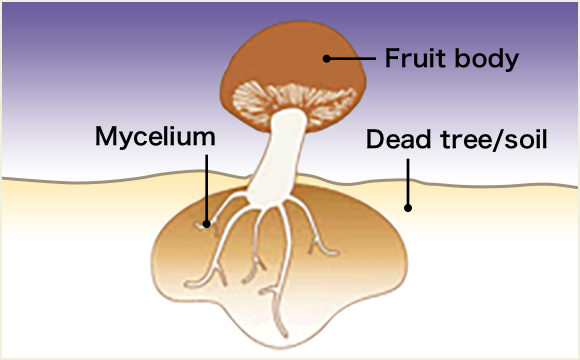
The mushroom life cycle begins with the airborne propagation of spores, which settle on dead trees or in soil and grow into a primary mycelium, which joins with another primary mycelium to form a secondary mycelium. This then expands by absorbing nutrients through its root to grow into the thick stem and cap shape which is generally known as a mushroom. This stem and cap part is called the fruit body, while the part that is rooted in the dead tree or the soil is called the mycelium.
Fruit body cultivation/mycelium cultivation
There are two ways of growing reishi mushrooms. One is to cultivate the fruit body and the other is mycelium cultivation. Nissan’s mushrooms are grown through fruit body cultivation under near natural conditions. Nissan Reishi is then made with rigorously selected fruit body specimens.
| Fruit body cultivation | The fruit body is cultivated over almost a full year, as in the natural world, before the essence is extracted. |
|---|---|
| Mycelium cultivation | The mycelium is grown artificially within a short timespan before the essence is extracted. |
Nissan Reishi fruit body cultivation
There are two ways of growing reishi mushrooms. One is to cultivate the fruit body and the other is mycelium cultivation. For Nissan Reishi, we emphasize cultivation of the fruit body, which allows the mushroom to mature steadily under near natural conditions. Nissan Reishi is then made with rigorously selected fruit body specimens.
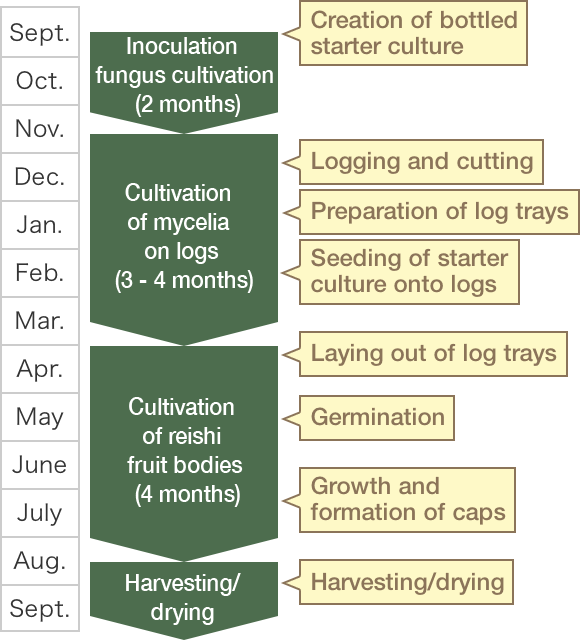
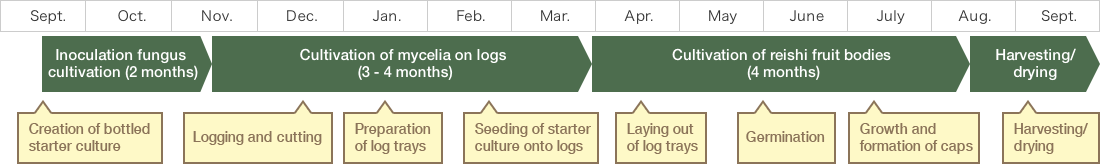
1Creation of bottled starter culture
The seed fungus is sown on a sawdust medium to create a bottled starter culture
2Logging and cutting
Trees from natural forest are felled and cut to log size
3Preparation of log container
The seed fungus is sown on logs and the logs placed in containers
4Log cultivation of mycelia
The mycelia are cultivated in an incubation room
5Laying down of log culture
The culture logs are laid out in a greenhouse under strictly controlled thermal and environmental conditions
6Germination
7Growth and formation of caps
8Harvesting/drying
The harvested mushrooms are dried and used as the main ingredient
Please note that applications will close once the planned number of samples has been distributed.
Your understanding is appreciated.
